Optical Instruments and Systems
A
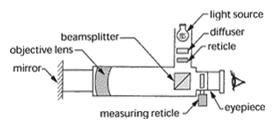
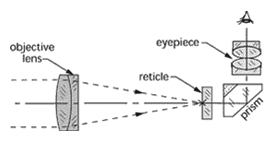
Alignment telescope – An optical tooling instrument consisting of an objective lens, a focusing lens, an optical micrometer, a reticle and an eyepiece. The alignment telescope projects a precise line of sight to which a number of targets at varying distances may be aligned accurately.
Anomaloscope – An optical instrument that uses a yellow light of varying intensity with red and blue lights of fixed intensity to test for colorblindness.
Autocollimator – A single instrument combining the functions of a telescope and a collimator to detect small angular displacements of a mirror by means of its own collimated light. It consists of a lens with an illuminated reticle. The reticle usually carries several parallel lines subtending known angles at the lens. An electronic autocollimator provides a continuous output voltage, the sign and amplitude of which are related to the angular displacement of the mirror.
Autocollimator
Autostigmatic microscope – The study of the interactions between sound waves and light in a solid medium.
B
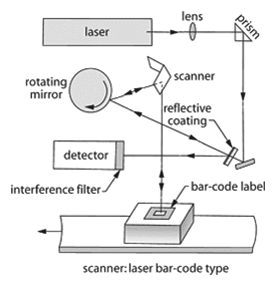
Barcode scanner – An optical scanning device designed to read information printed in the form of bars of different size by detection and processing of the varying reflectivity of light in the bar code.
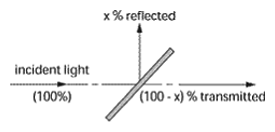
Beamsplitter – An optical device for dividing a beam into two or more separate beams. A simple beamsplitter may be a very thin sheet of glass inserted in the beam at an angle to divert a portion of the beam in a different direction. A more sophisticated type consists of two right-angle prisms cemented together at their hypotenuse faces. The cemented face of one prism is coated, before cementing, with a metallic or dielectric layer having the desired reflecting properties, both in the percentage of reflection and the desired color. In a color television camera, for example, a three-way beamsplitting prism is employed in which multilayer films are deposited on the interfaces to divert red and green light to two vidicons, leaving the blue image to pass through to the third vidicon tube.
Beamsplitter
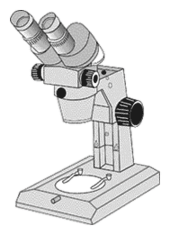
Binocular microscope – A microscope designed with two eyepieces (oculars), permitting the use of both eyes when viewing through the instrument.
Binocular microscope
Borescope – A device for the internal inspection of hard-to-get-at mechanical parts, such as rifle barrels, sewer pipes, oil wells, or gas mains. The long narrow tube used contains a telescope system with as many relay lenses as necessary. A lamp located in front illuminates the inside of the bore, and the inclusion of a small 45° mirror often permits detailed examination of the tube wall. Some small borescopes and most types of medical endoscopes are now equipped with a fiber optic bundle, for image and/or illumination transfer.
C
Camera – A light-tight box that receives light from an object or scene and focuses it to form an image on a light-sensitive material or a detector. The camera generally contains a lens of variable aperture and a shutter of variable speed to precisely control the exposure. In an electronic imaging system, the camera does not use chemical means to store the image, but takes advantage of the sensitivity of various detectors to different bands of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Camera
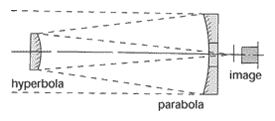
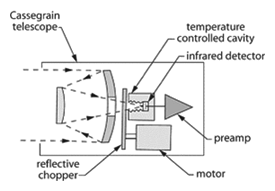
Cassegrain telescope – A two-mirror lens design used in astronomical telescopes, the primary being a parabola, the secondary a smaller hyperbola. The image formed is free of spherical aberration and color and is located behind the vertex of the primary.
Cassegrain telescope
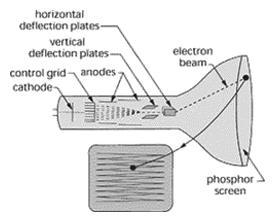
Cathode ray tube – A vacuum tube with an electron gun at one end and a fluorescent screen at the other. Electrons emitted from a heated filament are accelerated by a series of annular anodes at progressively higher positive voltages. The electron beam is then deflected by two pairs of electrostatically charged plates between the gun and the screen. Electromagnets are sometimes used in place of the deflector plates.
Cathode ray tube
Choledochoscope – A small fiber optic endoscope used in laser surgery.
Chromascope – An instrument designed to analyze the optical effects of color.
D
Detector – 1) A device designed to convert the energy of incident radiation into another form for the determination of the presence of the radiation. The device may function by electrical, photographic or visual means. 2) A device that provides an electric output that is a useful measure of the radiation that is incident on the device.
Digital camera – A camera that converts a collected image into pixels that are black or white digital or shades of gray. The digital data may then be manipulated to enhance or otherwise modify the resulting viewed image.
E
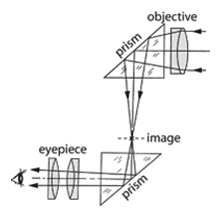
Elbow telescope – A refracting telescope that uses a prism to bend the line of sight 90°.
Elbow telescope
Electron microscope – A device utilizing an electron beam for the observation and recording of submicroscopic samples with the aid of photographic emulsions or other short-wavelength sensors. With the electron microscope, the maximum useful magnification is over 300,000.
Endoscope - A medical instrument used to view inside the human body by inserting the instrument into a natural or created aperture. The endoscope may use a coherent fiber optic bundle or conventional optics to relay the image to the eye or a television camera. Illumination is provided by a concentric bundle of noncoherent fiber optics.
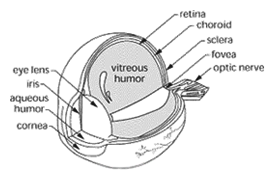
Eye – The organ of vision or light sensitivity.
Eye
F
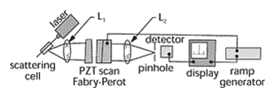
Fabry-Perot interferometer – A refracting telescope that yields an erect image by the use of a positive lens for its objective and a negative lens for its eyepiece.
Fabry-Perot interferometer
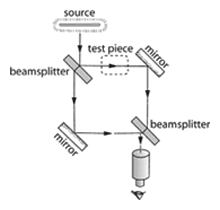
Fizeau interferometer – A type of interferometer noted for producing narrow multiple-beam interference fringes. As a result, when compared with the Twyman-Green, the Fizeau interferometer has fewer optical components, does not have the large beamsplitter and can be adjusted to a greater accuracy.
Fizeau interferometer
G
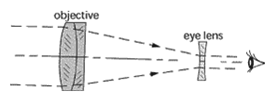
Galilean telescope – A refracting telescope that yields an erect image by the use of a positive lens for its objective and a negative lens for its eyepiece.
Galilean telescope
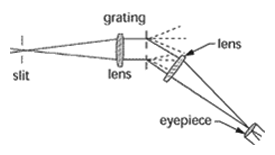
Grating – A framework or latticework having an even arrangement of rods, or any other long narrow objects with interstices between them, used to disperse light or other radiation by interference between wave trains from the interstices. The ability of a grating to separate wavelengths (chromatic resolving power) is expressed as being equal to the number of lines in the grating.
Grating spectroscope – A spectroscope having a diffraction grating for the resolution of light of various wavelengths.
Grating spectroscope
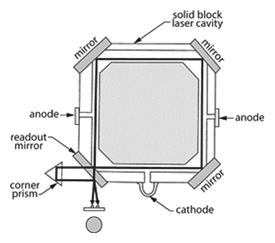
Gyroscope – 1) Ring Laser: A solid block of glass-ceramic material with holes drilled the length of all four sides, and mirrors attached to the corners to form a closed path, in which two independent laser beams oscillate at different frequencies. When the device is stationary, the optical paths traveled by the two beams are identical. Rotation of the cavity causes a difference in path length between the two beams that can be measured. 2) Fiber optic: An instrument to measure angular rotation, based on the principle that the application of force will alter the wavelength of light as it travels in one direction or the other around a coil of optical fiber wound on a drum, thus producing interference fringes at the termination of travel from which measurement can be made.
Gyroscope
H
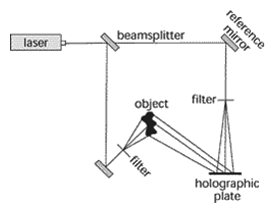
Hologram – An interference pattern that is recorded on a high-resolution plate, the two interfering beams formed by a coherent beam from a laser and light scattered by an object. After formation, if lit and viewed correctly, a 3-D image of the object is seen.
Hologram
I
Iconometer - An instrument in which an object's image, produced by a lens of known focal length, is used to determine the object's distance from the instrument when its size is known, or the object's size if the object-instrument distance is known.
Integrating sphere – A hollow sphere coated internally with a white diffusing material and provided with openings for incident beam, specimen and detector used for measuring the diffuse reflectance or transmittance of objects.
Interferometer – An instrument that employs the interference of lightwaves to measure the accuracy of optical surfaces. It can measure a length in terms of the length of a wave of light.
K
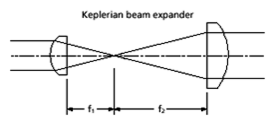
Keplerian telescope – A simple form of astronomical telescope that uses a fixed objective and a focusable eyepiece. The objective forms an intermediate image in the instrument, resulting in an image that appears upside down when viewed through the eyepiece.
Keplerian telescope
L
Laser – An acronym of Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. A laser is a cavity, with plane or spherical mirrors at the ends, that is filled with lasable material. This is any material -- crystal, glass, liquid, dye or gas -- the atoms of which are capable of being excited to a semistable state by light or an electric discharge. The light emitted by an atom as it drops back to the ground state releases other nearby, excited atoms, the light being thus continually increased in intensity as it oscillates between the mirrors. If one mirror is made to transmit 1 or 2 percent of the light, a brilliant beam of highly monochromatic, coherent radiation is emitted through the mirror. If plane mirrors are used, the beam is highly collimated. With concave mirrors, the beam appears to emerge from a point source near one end of the cavity.
Laparoscope – An endoscopic surgical instrument that includes a channel for the introduction of supplementary instruments.
Local area network – Data communications network in a clearly defined geographical location, and extending no more than a few miles in length. It generally takes in an office building or group of buildings, a campus or the like, offering many nodes and connecting computers and peripherals with high-capacity links.
M
Mach-Zender interferometer – An interferometer derived from the Twyman-Green interferometer. Light passing through a sample region in one direction recombines with a second leg without traversing the sample twice. The instrument is used to study transparent objects and is particularly useful in studying wind tunnel gas dynamics.
Mach-Zender interferometer
Magnifier – A lens or lens system that produces an enlarged virtual image of an object placed near its front focal point.
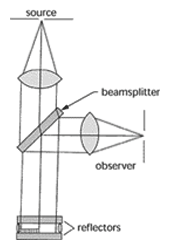
Michelson interferometer – It produces interference fringes by splitting a beam of monochromatic light so that one beam strikes a fixed mirror and the other a movable mirror. When the reflected beams are brought back together, an interference pattern results.
Michelson interferometer
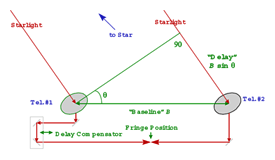
Michelson Stellar interferometer – An interferometer constructed to be positioned on a telescope to measure the angular separation of the components of double stars.
Michelson Stellar interferometer
Microscope – An instrument consisting of essentially a tube 160mm long, with an objective lens at the distant end and an eyepiece at the near end. The objective forms a real image of the object in focal plane of the eyepiece where it is observed by the eye. The total magnification is equal to the linear magnification of the objective multiplied by the magnifying power of the eyepiece.
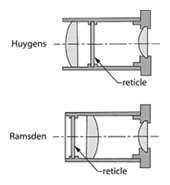
Microscope eyepiece – An eyepiece located at the near end of the microscope tube. It often is a simple Huygens eyepiece, but compensating and flat-field projection eyepieces are quite efficient. Negative eyepieces are sometimes used as projection relay lenses in photomicrography.
Microscope eyepiece
Modulator – A device that varies the amplitude and phase of a light beam; e.g., from a laser or by sound waves. Also known as a Bragg cell.
Monochrometer – An instrument for isolating narrow portions of the spectrum by using a prism or grating.
N
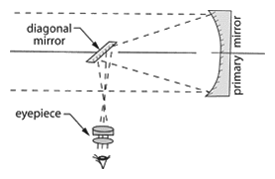
Newtonian telescope – A telescope with a concave paraboloidal objective mirror and a small plane (diagonal) mirror that reflects rays from the primary mirror laterally outside the tube where the image is viewed with an eyepiece.
Newtonian telescope
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) – A phenomenon, exploited for medical imaging, in which the nuclei of material placed in a strong magnetic field will absorb radio waves supplied by a transmitter at particular frequencies. The energy of the radio-frequency photons is used to promote the nucleus from a low-energy state, in which the nuclear spin is aligned parallel to the strong magnetic field, to a higher-energy state in which the spin is opposed to the field. When the source of the radio waves is turned off, many nuclei will revert to the lower state by emitting photons at the characteristic resonance frequencies, providing information about the sample material. Because the single protons in biologically abundant hydrogen atoms react well to the technique, it can produce excellent cross-sectional images of bone marrow and tissue.
O
Optical Coherence Testing (CAT scan) – A medical diagnosis technique that uses lightwaves to form cross-sectional images of a patient's retina or body.
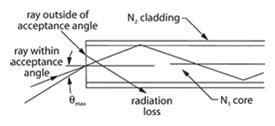
Optical fiber - A thin filament of drawn or extruded glass or plastic having a central core and a cladding of lower index of refraction to promote internal reflection.
Optical fiber
Otoscope – A light-conducting and imaging system used to inspect the inner ear.
Otoscope

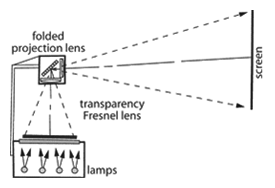
Overhead projector – A projector used to project transparencies. A horizontal 8 x 10-in. stage for writing or laying down preformed transparencies is provided with either an elliptical mirror or a plastic Fresnel lens below the stage to form an image of a lamp filament in the projection lens situated above the stage. A 45° mirror above or below the lens turns the vertical beam into a horizontal direction toward the screen behind the lecturer's head. The imagery is such that when the speaker is facing the audience, his normal writing on the stage appears erect and correct on the screen.
Overhead projector
P
Periscope – An optical instrument designed to displace the line of sight in a vertical direction. Used often in submarines.
Periscope
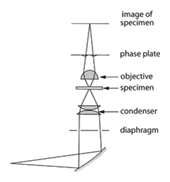
Phase-contrast microscope – A microscope that has an annular stop in the lower focal plane of the condenser, and a quarter-wave retarding and absorbing ring in the upper focal plane of the objective that just fills the image of the annular substage stop. Direct light passing through a transparent object falls on the ring where it is retarded by a quarter-wave and reduced in intensity. Light diffracted by the phase differences in the transparent object because of variations in refractive index and/or thickness, misses the retardation ring and interferes with the direct light in the manner of an interference microscope. This leads to an image in which variations of phase in the object appear as variations in brightness.
Phase-contrast microscope
R
Radiometer – A device used to measure the intensity of radiant energy.
Radiometer
Refractometer – An instrument used to measure the refractive index of solids and liquids. Several types exist, the most common being the Abbe refractometer.
S
Sagnac interferometer – A type of interferometer in which two coils of optical fiber are arranged so that light from a single source travels clockwise in one, and counterclockwise in the other. Rotation of the coils causes a phase shift in the combined output measured by the detector.
Sagnac interferometer
Scanner – 1) A device used to trace out an object and build up an image. One of the most common of these types is video scanning. The scanning takes place inside the television tube as electrons, guided by electron optics, sweep linearly across a tube face coated on the inside with a phosphorescent material. A scanner can convert a paper drawing or photograph into pixels on a display screen. Scanners are also used to relay information in optical data processing. 2) A device that automatically measures or checks a process or condition and may initiate a desired corrective action by means of switching. 3) A device for sensing recorded data, such as a supermarket bar code.
Scanner
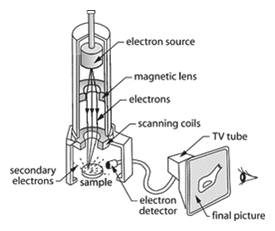
Scanning electron microscope – An electron microscope that uses a beam of electrons — accelerated to high energy and focused on the sample — to scan the sample surface, ejecting secondary electrons that form the picture of the sample.
Scanning electron microscope
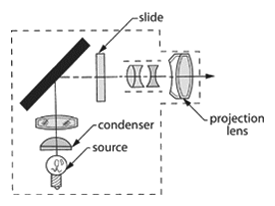
Slide projector – An optical projection device designed to project positive color transparencies onto a screen for viewing.
Slide projector
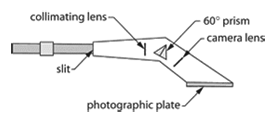
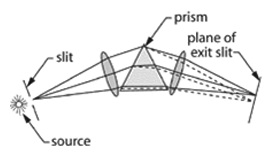
Spectrograph – An optical instrument for forming the spectrum of a light source and recording it on a film. The dispersing medium may be a prism or a diffraction grating. A concave grating requires no other means to form a sharp image of the slit on the film, but a plane grating or a prism requires auxiliary lenses or concave mirrors to act as image-forming means in addition to the dispersing element. Refracting prisms can be used only in parallel light, so a collimating lens is required before the prism and an imaging lens after it. Some special-purpose spectrographs are equipped with tiny photodetectors situated in the spectrum at the positions corresponding to the lines of elements whose presence is to be determined.
Spectrograph
Spectrometer – A kind of spectrograph in which some form of detector, other than a photographic film, is used to measure the distribution of radiation in a particular wavelength region.
Spectrometer
Spectrophotometer – An instrument for measuring spectral transmittance or reflectance.
Spectroscope - In a general sense, any one of a class of instruments used to disperse radiation, visible or invisible, into its component wavelengths and for determining or measuring the resultant spectrum. In a limited sense, the instrument is capable of being used only for visual observation of the spectrum.
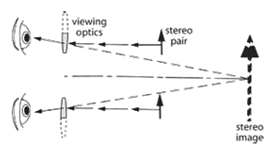
Stereoscope - A small instrument containing a picture support and a pair of magnifying lenses so arranged that the left eye sees only the picture taken with the left lens of the stereo camera, and the right eye only the right picture. If the camera lenses are separated by the interocular distance, and if the focal lengths of camera and stereoscope lenses are equal, then a true-to-scale or orthoscopic reproduction of the scene is obtained. Stereoscopes are used extensively in photogrammetry.
Stereoscope
T
Trinoscope – A color-television viewing system with three kinescopes, three lenses and three deflection yokes used to form the red, green and blue images required for a tricolor television projection.
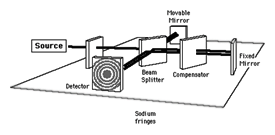
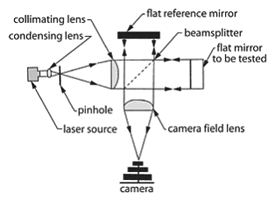
Twyman-Green interferometer - A testing device that provides a contour map of the emergent wavefront for the observer in terms of the given wavelength of the light.
Twyman-Green Interferometer
W
Waveguide – A system or material designed to confine and direct electromagnetic waves in a direction determined by its physical boundaries.
Compiled with help from: OSA Student Chapter Members, using the following websites: UCL Physics & Astronomy - Condensed Matter & Materials Physics, Galilean and Keplerian Telescopes, Hyper Physics, Standard Medical Limited, Photonics Dictionary, SMART sense.