Prisms
A
Abbe prism - A particular form of roof prism that can be used to invert an image. Because of the perpendicular end faces, it can be inserted between the objective and eyepiece of a telescope. If the roof is replaced by a plane surface, it becomes a reversion, or K, prism.
Abbe prism
Achromatic prism - A combination of two prisms, one of high-dispersion glass, the other of low-dispersion glass, which produces an angular deviation of a light beam without introducing any chromatic dispersion.
Achromatic prism
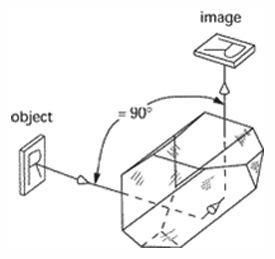
Amici prism - Also known as roof prism. A type of prism designed by G.B. Amici. It consists of a roof edge produced upon the long reflecting face of a right-angle prism. Used as an erecting system in elbow and panoramic telescopes. It erects the image and bends the line of sight through a 90° angle. Also known as a roof prism.
Amici prism
C
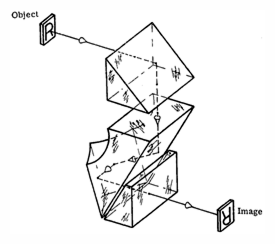
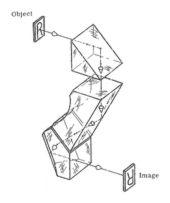
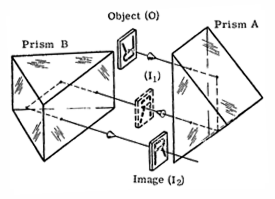
Carl Zeiss prism system - This system consists of three single prisms which invert and revert the image, but will not deviate the line of sight. The line of sight is displaced by an amount depending on the distance between the first and second prisms.
Carl Zeiss prism system
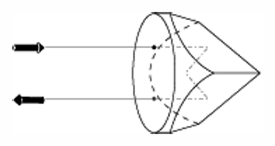
Corner cube prism - aka corner cube reflector, corner reflector. A prism having three mutually perpendicular surfaces and a hypotenuse face. Light entering through the hypotenuse is reflected by each of the three surfaces in turn and will emerge through the hypotenuse face parallel to the entering beam. The prism thus returns entering beams to the source. Also may be constructed from three first-surface mirrors.
Corner cube prism
Cornu-Jellet prism - A prism formed by dividing a Nicol prism in a plane parallel to the path of vibration of the transmitted light and taking out the wedge-shaped piece. After the pieces are rejoined, the planes of vibration of the transmitted light of the two halves form a small angle with each other.
Cornu double prism - A compound prism formed by cementing together two 30° prisms, one of right-handed and one of left-handed quartz. It has good ultraviolet-transmitting qualities and no double refraction.
Cornu double prism
Crossed prisms - The positioning of two Nicol prisms so that their axes are at right angles to each other. With this arrangement, light transmitted by one prism will not be transmitted by the other.
D
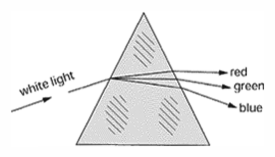
Direct-vision prism - An assembly of multiple prisms that disperses incident light into its spectral components without deviating light at the central wavelength.
Direct-vision prism
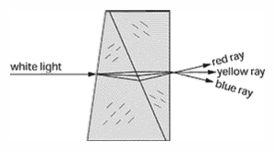
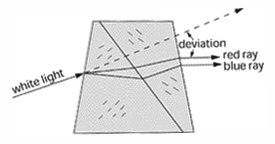
Dispersing prism - A prism or series of prisms used to disperse a beam of radiant energy of mixed wavelengths into its spectral components.
Dispersing prism
Dove prism - A form of prism invented by H.W. Dove. It resembles half of a common right-angle prism in which a ray entering parallel to the hypotenuse face is reflected internally at that face and emerges parallel to its incident direction. One of the incident rays emerges along a continuation of its incident direction, and if the prism is rotated about that ray through some angle, the image rotates through twice that angle. A Dove prism must be used in parallel light.
Dove prism
F
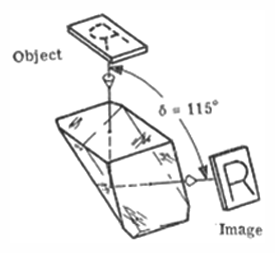
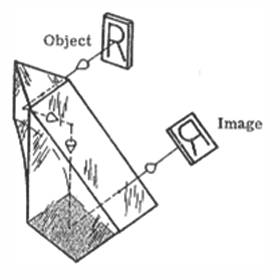
Frankford Arsenal prism number 1 - This prism will revert the image and, at the same time, it will deviate the line of sight by 115 degrees.
Frankford Arsenal prism number 1
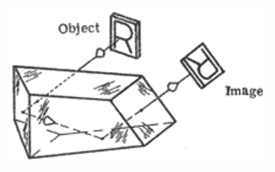
Frankford Arsenal prism number 2 - This prism inverts and reverts the image and deviates it by 60 degrees.
Frankford Arsenal prism number 2
Frankford Arsenal prism number 3 - This prism deviates the line of sight by ninety degrees in the horizontal plane and through an angle of forty-five degrees in an upward direction. An observer standing at a right angle to the line of sight will see an inverted and reverted image.
Frankford Arsenal prism number 3
Frankford Arsenal prism number 4 - In this prism, the line of sight is deviated by ninety degrees in the horizontal plane and by forty-five degrees in the vertical plane simultaneously. An observer standing at a right angle to the line of sight will see a reverted image.
Frankford Arsenal prism number 4
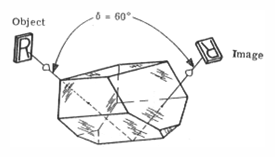
Frankford Arsenal prism number 5 - The line of sight is deviated by ninety degrees in the horizontal plane and by sixty degrees in the vertical plane in this prism. An observer standing at a right angle to the line of sight will see an inverted and reverted image.
Frankford Arsenal prism number 5
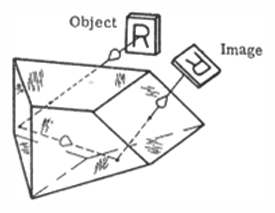
Frankford Arsenal prism number 6 - In this prism, the line of sight is deviated by ninety degrees in the horizontal plane and by sixty degrees in the vertical plane simultaneously. The prism inverts the image.
Frankford Arsenal prism number 6
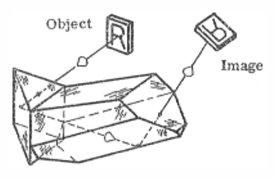
Frankford Arsenal prism number 7 - In this prism, the line of sight is deviated by ninety degrees in the horizontal plane and by forty-five degrees in the vertical plane simultaneously. An observer standing at a right angle to the line of sight will see a normal image of the target since the prism neither inverts nor reverts the image.
Frankford Arsenal prism number 7
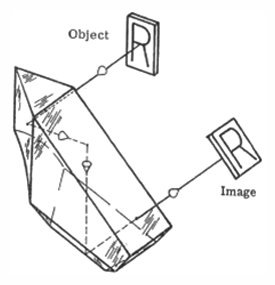
Foucault prism - A polarizing prism formed from calcite that is like the Nicol prism but has the two parts divided by a thin air-film and cut to such angles that the extraordinary beam will be transmitted and the ordinary beam totally reflected. However, part of the extraordinary beam will be reflected, making the Foucault prism somewhat less efficient than the Nicol.
G
Glan-Thompson prism - aka Glan prism. The Glan-Foucault prism achieves polarization by removing one plane of polarization by total internal reflection. It is made of two prisms of calcite with no other intervening material, i.e., with air between them.
Glan-Thompson prism
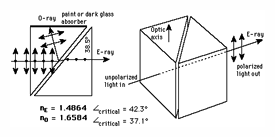
Goerz prism system - This prism system consists of three single prisms as illustrated below. The system inverts and reverts the image. The image is also displaced by an amount depending on the distance between the first and second prisms.
Goerz prism system
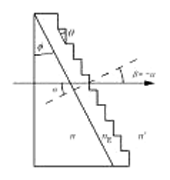
Grating prism - A specific, right-angle prism having a transmission grating replicated on its hypotenuse face and used in applications requiring a system that can produce in-line viewing for one wavelength.
Grating prism
J
Jellet prism - A prism produced by severing a Nicol prism and reconstructing the polarization angles of the two halves so that they are slightly wedged toward each other.
L
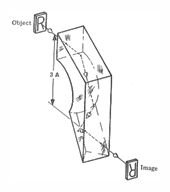
Leman prism - This prism inverts and reverts the image while laterally shifting the image by an amount equal to 3A, as shown in the figure.
Leman prism
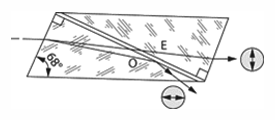
Lippich prism - A small half-shade analyzer placed in the eyepiece of a polarimeter to determine the character of the polarized light emitted by the instrument. It consists of a Nicol prism situated so that it covers half of the eyepiece's field of view.
N
Nicol prism - A prism invented by William Nicol in 1828 that is made of calcite, the end faces of which are ground to an angle of 68° between one vertical side and the end surface. The prism is cut diagonally in half, the cut being made at right angles to the shorter diagonal of the end face. The parts are then cemented together. Unpolarized light striking an end face is polarized to vibrate in two directions. The extraordinary ray passes through the crystal, and the ordinary ray is reflected to one side at the calcite-balsam interface and is lost.
Nicol prism
O
Ocular prism - The prism used in a rangefinder to bend the lines of sight through the instruments into the eyepieces.
Offset prism - A prism or prism assembly that serves to displace the instrument's optical axis.
Offset prism
P
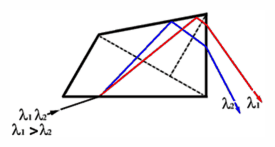
Pellin-Broca prism - A form of dispersing prism, often used in monochromators, that consists of a common right-angle prism with a 30° dispersing prism attached to each of its square faces. The spectrum formed by the prism is the same as if the two 30° prisms were joined together to form a single 60° prism. The particular ray that would pass through the 60° prism in minimum deviation is turned through a right angle in the Pellin-Broca prism, for which reason the latter often is referred to as a constant deviation prism. When this prism is rotated about an axis parallel to the refracting edges, the spectrum moves laterally past the exit slit of a monochromator.
Pellin-Broca prism
Penta prism - A five-sided prism containing two reflecting surfaces at 45° to each other, and two refracting faces perpendicular to the entering and emerging beams. The deviation angle of 90° is independent of any rotation of the prism about an axis parallel to the line of intersection of the two reflecting faces. It is commonly used as an end-mirror in a rangefinder and as an "optical square'' in surveying and alignment machinery.
Penta prism
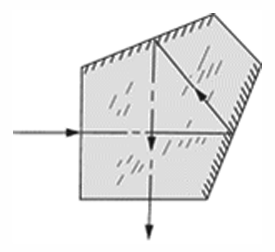
Pechan prism - A prism made up of two air-spaced components. It has the ability to revert, and not invert, an image, and can be used in convergent, divergent and parallel light. May be rotated to compensate for image rotation.
Pechan prism
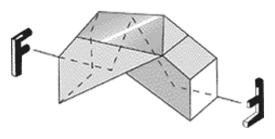
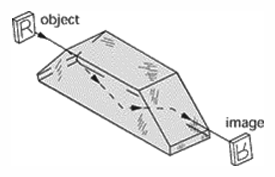
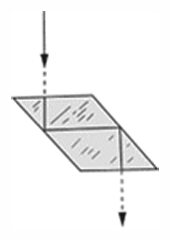
Porro prism - A 45°-90°-45° reflecting prism whose surfaces form the 90° angle reflecting the light beam through a total angle of 180°. Two of these prisms are used in succession in a prism binocular. For each set of prisms as shown below, the image in both inverted and reverted.
Porro prism
Prism - A transparent optical element having at least two polished plane faces inclined relative to each other, from which light is reflected or through which light is refracted.
Prism
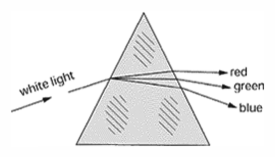
R
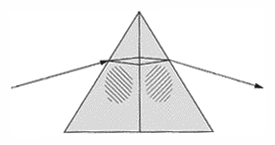
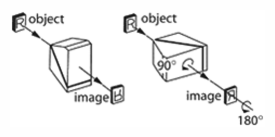
Right angle prism - This prism deviates the line of sight by ninety degrees. The image will appear inverted when the prism is held before the eye as shown on the left. The image will appear reverted if the prism is rotated as shown in the image on the right below.
Right angle prism
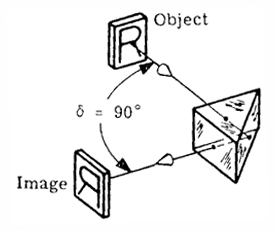
Reflecting prism - A prisms have several plane polished surfaces, some to transmit light, some to reflect light, and some to serve both functions in succession. Reflecting prisms are those in which one or more internal reflections of the rays take place. An example is the Dove prism.
Rhomboid prism - A reflecting prism that is rhomboidal in shape. It has two parallel transmitting faces, and two parallel reflecting faces; the latter are oblique to the former (usually but not necessarily at 45°). This prism is capable of offsetting the optical axis without changing the aspect of the image. If the rhomboid prism is rotated around an axis normal to the entrance surface, the offset emergent axis can be moved parallel to itself in a circular arc; hence pairs of these prisms often are used to provide interpupillary adjustment of the eyepiece of binocular instruments such as stereoscopic rangefinders and heightfinders.
Rhomboid prism
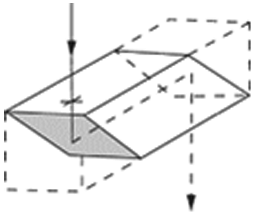
Risley prisms - An assembly consisting of two thin prisms in series. Counterrotation of the prisms changes the magnitude of beam deviation, while rotating them together changes deviation azimuth. The two prisms are usually identical. The examples below show two of many options.
Risley prisms
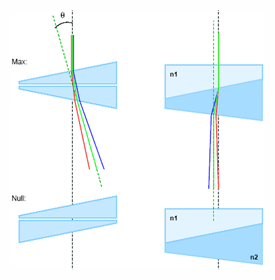
S
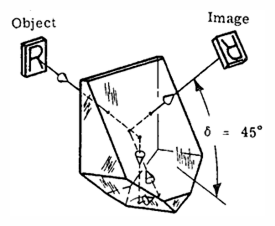
Schmidt prism - This prism reverts the image while deviating the line of sight by forty-five degrees.
Schmidt prism
W
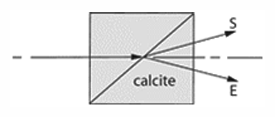
Wollaston prism, 1st definition - A polarizing prism consisting of two calcite prisms cemented such that they deviate the two emerging beams (which are mutually perpendicularly polarized) by nearly equal amounts in opposite directions.
Wollaston prism, 1st definition
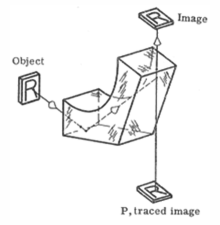
Wollaston prism, 2nd definition - This prism neither inverts nor reverts the image, but will deviate a beam by ninety degrees. IT is used in an instrument known as a "camera Lucida" or "Camera Clara."
Wollaston prism, 2nd definition
Compiled with help from: OSA Student Chapter Members, using the following websites: Photonics Dictionary, Military Handbook: Optical Deign of Elements, Vol. 1, 1959, Melles Griot, and Hyper Physics.